Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are a prevalent global health concern, affecting individuals of all ages and backgrounds. These infections can have serious health consequences if left untreated, making it essential to be informed about their symptoms and seek appropriate medical attention. In this article, we will discuss the most common STIs and their associated symptoms, providing valuable knowledge for prevention, early detection, and timely treatment.
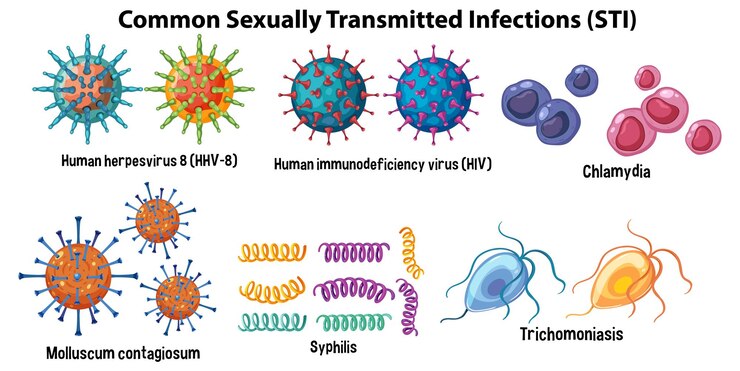
- Chlamydia: Chlamydia is one of the most common bacterial STIs worldwide. It often exhibits no noticeable symptoms, particularly in women, which makes it important to undergo regular STI screenings. When symptoms are present, they may include abnormal vaginal discharge, pain or burning during urination, and lower abdominal pain.
- Gonorrhea: Gonorrhea is another bacterial STI that can affect both men and women. Symptoms may include a thick, cloudy, or bloody discharge from the penis or vagina, painful urination, and increased frequency of urination. In some cases, gonorrhea may cause rectal or throat infections, leading to symptoms such as rectal pain, discharge, or a sore throat.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV): HPV is a viral infection that commonly spreads through sexual contact. Many people with HPV may not exhibit any symptoms, but certain strains of the virus can cause genital warts. These warts may appear as small, flesh-colored bumps or clusters in the genital or anal area. In some cases, HPV can also lead to cervical, vaginal, or anal cancer.
- Genital Herpes: Genital herpes is caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). Symptoms typically include the presence of painful, fluid-filled blisters or sores in the genital area. These outbreaks may be accompanied by itching, burning sensations, and flu-like symptoms such as fever and swollen lymph nodes. It is important to note that herpes can still be transmitted even in the absence of visible sores.
- Syphilis: Syphilis is a bacterial infection that occurs in stages. In the early stages, symptoms may include painless sores or ulcers (known as chancres) in the genital area, rectum, or mouth. If left untreated, syphilis can progress to the secondary stage, marked by a rash on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, along with flu-like symptoms. Late-stage syphilis can lead to severe complications, affecting the heart, brain, and other organs.
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV): HIV attacks the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to various infections and diseases. In the early stages, symptoms may be similar to those of the flu, including fever, fatigue, sore throat, and swollen lymph nodes. As the infection progresses, more severe symptoms such as weight loss, persistent diarrhea, and opportunistic infections may occur.
- Trichomoniasis: Trichomoniasis is a common STI caused by a parasite. Symptoms in women may include itching, redness, and swelling of the genital area, as well as abnormal vaginal discharge with a strong odor. Men with trichomoniasis may experience itching or irritation inside the penis, discharge from the penis, or a burning sensation after urination or ejaculation.
It is important to note that the presence or absence of symptoms does not always indicate the presence or absence of an STI. Many individuals may be asymptomatic carriers and unknowingly transmit infections to their partners. Regular STI testing and open communication with sexual partners are key steps in preventing the spread of infections and protecting your sexual health.
If you experience any symptoms or are concerned about potential exposure to an STI, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for proper testing, diagnosis, and treatment. Early detection and appropriate medical care not only help manage the infection but also prevent further complications and protect both your own health and the health of your sexual partners.
Remember, practicing safe sex by using condoms consistently and correctly, limiting sexual partners, and engaging in open and honest communication about sexual health are vital steps in reducing the risk of STIs. Empower yourself with knowledge, prioritize regular STI screenings, and take proactive measures to protect your sexual well-being.